Substance abuse affects nearly every part of the body, but one area that often goes unnoticed is the eyes. Vision is something most people take for granted—until it starts to fade. The reality is that drugs and alcohol can have devastating effects on eye health, leading to gradual or even sudden vision loss. Whether through direct toxicity, nutritional deficiencies, or increased risk of injury and infection, substance abuse poses a serious threat to one of our most vital senses.
The Eyes: A Window Into Your Health
The eyes are more than just organs for sight; they are indicators of overall health. When substances like alcohol, opioids, stimulants, or inhalants are used frequently, they can directly damage the eyes or indirectly affect vision through systemic harm. Blood vessels in the eyes, the optic nerve, and even the muscles controlling eye movement are all vulnerable to the effects of toxic substances.
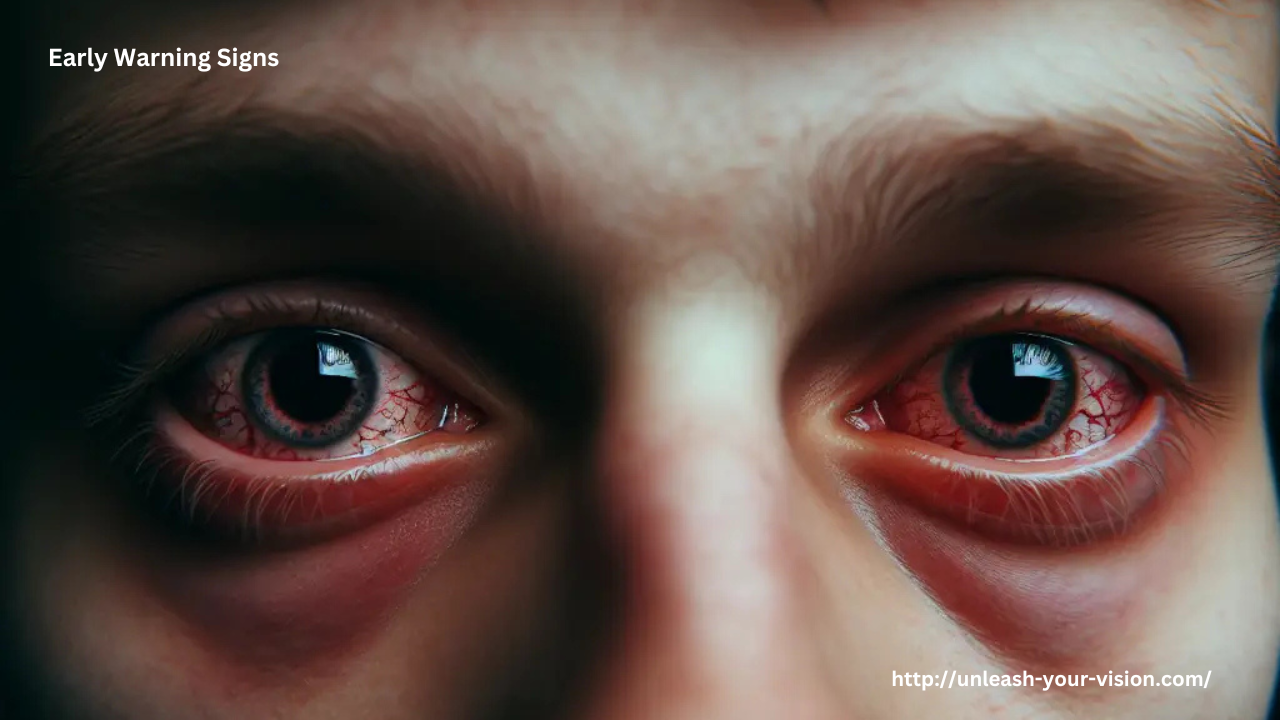
Immediate Symptoms: Warning Signs Often Ignored
In the early stages of substance use, users may experience symptoms that seem mild or temporary: bloodshot eyes, blurry vision, light sensitivity, or pupil changes. Alcohol and marijuana, for example, dilate blood vessels in the eyes, causing redness. Cocaine and methamphetamine can lead to dry eyes and involuntary eye movements, impairing focus and coordination.
These signs might fade after the high wears off, but repeated exposure increases the risk of long-term damage. Unfortunately, because these symptoms are easy to dismiss, they often go untreated until more serious conditions arise.
Long-Term Consequences: Vision Loss Becomes Permanent
Prolonged substance abuse can lead to a range of serious eye disorders, many of which result in partial or complete vision loss:
-
Optic Neuropathy
Toxic substances like meth, alcohol, and heroin can damage the optic nerve—the critical pathway between the eye and the brain. This condition, known as toxic optic neuropathy, reduces color perception and central vision. Left untreated, it can lead to irreversible blindness. -
Retinal Damage
Stimulants such as cocaine and meth can cause a sudden increase in blood pressure, damaging the tiny vessels in the retina. This can lead to retinal hemorrhages, scarring, or detachment. Retinal detachment, in particular, is a medical emergency that can permanently destroy vision in the affected eye. -
Cataracts and Accelerated Aging
Chronic alcohol use and smoking can speed up the development of cataracts—clouding of the eye’s lens that impairs vision. People struggling with addiction often experience this condition earlier in life compared to the general population. -
Nutritional Deficiencies
Substance abuse frequently leads to poor nutrition, which affects eye health. A lack of essential nutrients such as Vitamin A, B12, and folic acid can result in night blindness, dry eye syndrome, and nerve damage.
Prevention and Recovery
The most effective way to protect your eyesight is to avoid or stop using harmful substances. For those already struggling with addiction, seeking help from medical professionals and addiction specialists can slow or even reverse some of the damage. Regular eye exams, proper nutrition, and hydration can also aid in recovery.
Conclusion
Vision loss from substance abuse is real, serious, and often irreversible. By understanding these eye-opening truths and raising awareness about the risks, individuals can take steps to protect their vision and overall health. Recovery is possible—and with it, the chance to see the world clearly once again.